
MATLAB opens the Manage Files Using Source Control dialog box.
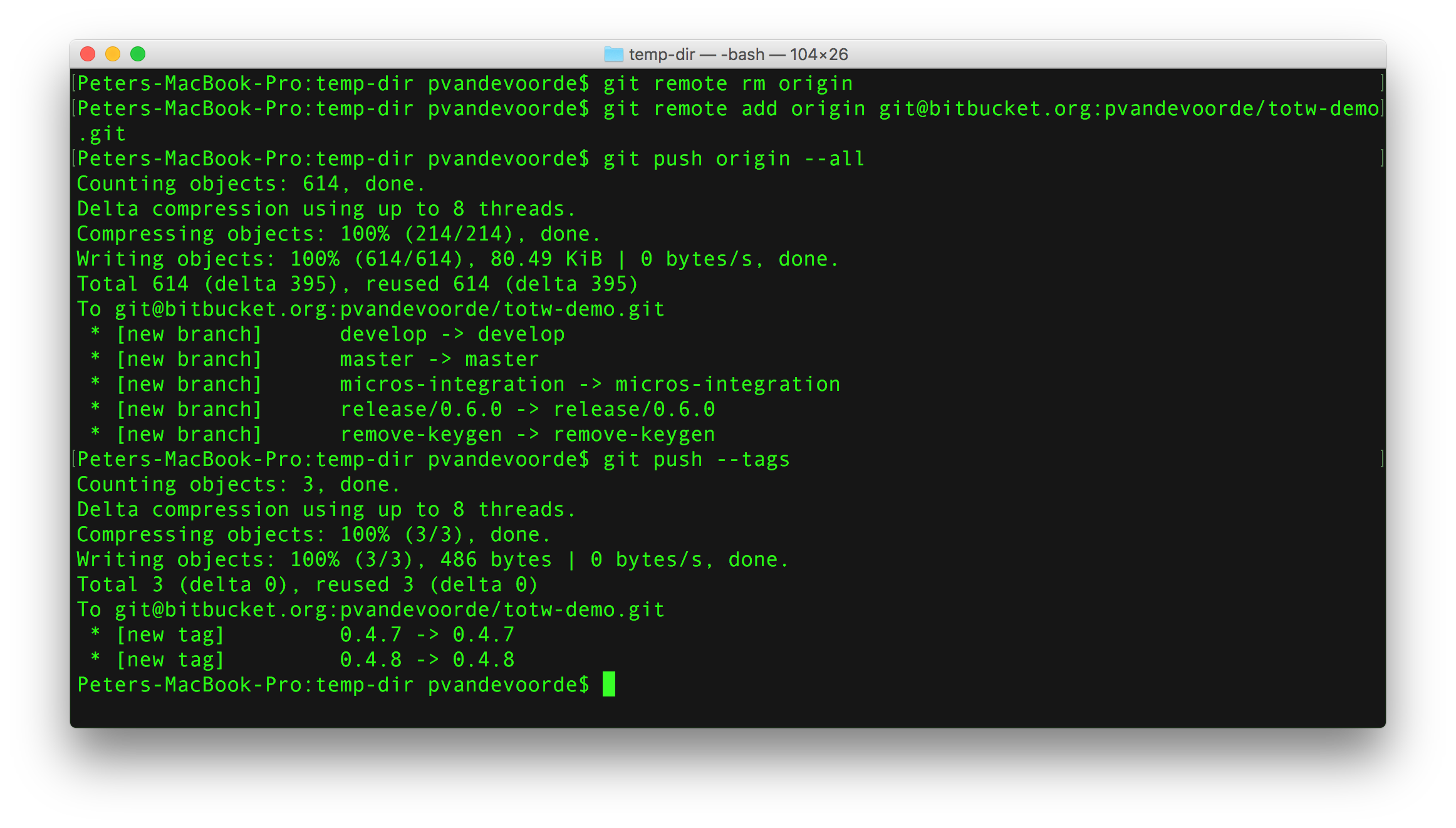
git push -u origin master: When pushing a branch for the first time, this type of push will configure the relationship between the remote and your local repository so that you can use git pull and git push with no additional options in the future.In the Current Folder browser, right-click the white space and select Source Control > Manage Files.git push: Uploads all local branch commits to the remote.git remote add origin : Add a remote so you can collaborate with others on a newly initialized repository.git remote -v: Show the associated remote repositories and their stored name, like origin.git status: Always a good idea, this command shows you what branch you're on, what files are in the working or staging directory, and any other important information.git clone : Clone (download) a repository that already exists on GitHub, including all of the files, branches, and commits.Return to your working repository, the one that you expect to be under version control. (It could be possible that multiple layers of. Run git status again to confirm that Git is no longer tracking any of these files. git directory, effectively un-initializing that repository.

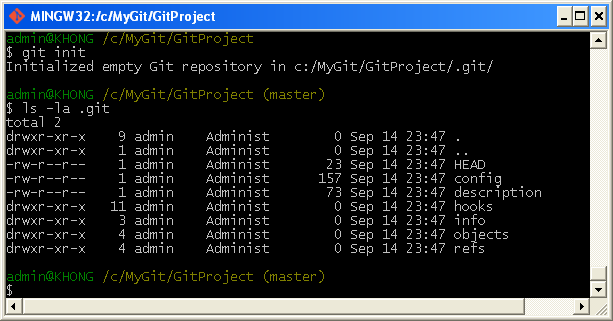
git directory, and you are sure that you don't want that to be a Git repository, use rm -rf. Use git status again in combination with ls -al. If you don't see it, navigate one level up in the directory structure with cd. If it is, you can either run ls -al and look for an otherwise hidden. Use git status to see if the current directory is tracked by Git. To fix this, you first need to track down which directory is the unintended repository. Maybe you suspect that another parent directory is also a Git repository. You may have noticed strange error messages when using Git. Running git init in the wrong place will create unintended repositories. git init Gone Wrong git init in the wrong directory Use git init and specify which directory to turn into a Git repository. Or, you can create a new repository in a directory in your current path. For an existing project to become a Git repository, navigate into the targeted root directory. The default behavior of git init is to transform the current directory into a Git repository. Then, your team can interact with the repository without git init again. git add, git commit, and git push to create a history that makes sense for the beginning of your project. Then, move the project's files into that cloned repository. If there are commits and files in the remote repository but you would still like it to contain your project files, git clone that repository. If there are no commits in the remote repository, you can follow the steps above for git init. If you create a remote repository first with the intent of moving your project to it later, you may have a few other steps to follow. If the repository already exists on a remote, you would choose to git clone and not git init.
Shape your history into at least one commit by using git add to stage the existing files, and git commit to make the snapshot.This stores the remote URL under a more human-friendly name, origin. Then, add the remote URL to your local git repository with git remote add origin.Once you have initialized the repository, create a remote repository somewhere like.First, initialize the repository and make at least one commit.This is only run once, even if other collaborators share the project. git init is probably the right choice for you. Your project may already exist locally, but it doesn't have Git yet. git init: One Person Starting a New Repository Locally Sometimes, it's unclear if you should use git init, git clone, or both. Examples of git init git init vs git clone You can see all of the options with git init in git-scm's documentation. git init -bare: Create a new bare repository (a repository to be used as a remote repository only, that won't contain active development).git init : Transform a directory in the current path into a Git repository.git init: Transform the current directory into a Git repository.
#GIT ADD REMOTE AND INIT HOW TO#
How to Use git init Common usages and options for git init git directory is what separates a regular directory from a Git repository. That directory stores all of the objects and refs that Git uses and creates as a part of your project's history. To initialize a repository, Git creates a hidden directory called. To start a repository, use either git init or git clone - not both. Git init is one way to start a new project with Git. Git init turns any directory into a Git repository.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
